要复现这个漏洞必须对Turbofan的Simplified Lowering阶段和Deoptimization阶段有一定的了解。
首先熟悉一下这个issue的poc,下面的所有的分析都是以这个poc为基础来进行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
// Copyright 2019 the V8 project authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
// Flags: --allow-natives-syntax --opt --no-always-opt
let g = 0;
function f(x) {
let y = BigInt.asUintN(64, 15n);
// Introduce a side effect to force the construction of a FrameState that
// captures the value of y.
g = 42;
try {
return x + y;
} catch(_) {
return y;
}
}
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(f);
assertEquals(16n, f(1n));
assertEquals(17n, f(2n));
%OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall(f);
assertEquals(16n, f(1n));
assertOptimized(f);
//the deoptimization reason is that the add's operand
//change from BigInt to smi.
assertEquals(15n, f(0));
assertUnoptimized(f);
漏洞原理
问题发生在SL阶段对于FrameState Node的处理上,下面是SL阶段对于FrameState Node访问函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
void VisitFrameState(Node* node) {
DCHECK_EQ(5, node->op()->ValueInputCount());
DCHECK_EQ(1, OperatorProperties::GetFrameStateInputCount(node->op()));
ProcessInput(node, 0, UseInfo::AnyTagged()); // Parameters.
ProcessInput(node, 1, UseInfo::AnyTagged()); // Registers.
// Accumulator is a special flower - we need to remember its type in
// a singleton typed-state-values node (as if it was a singleton
// state-values node).
if (propagate()) {
EnqueueInput(node, 2, UseInfo::Any());
} else if (lower()) {
Zone* zone = jsgraph_->zone();
Node* accumulator = node->InputAt(2);
if (accumulator == jsgraph_->OptimizedOutConstant()) {
node->ReplaceInput(2, jsgraph_->SingleDeadTypedStateValues());
} else {
ZoneVector<MachineType>* types =
new (zone->New(sizeof(ZoneVector<MachineType>)))
ZoneVector<MachineType>(1, zone);
(*types)[0] = DeoptMachineTypeOf(GetInfo(accumulator)->representation(),
TypeOf(accumulator));
node->ReplaceInput(
2, jsgraph_->graph()->NewNode(jsgraph_->common()->TypedStateValues(
types, SparseInputMask::Dense()),
accumulator));
}
}
ProcessInput(node, 3, UseInfo::AnyTagged()); // Context.
ProcessInput(node, 4, UseInfo::AnyTagged()); // Closure.
ProcessInput(node, 5, UseInfo::AnyTagged()); // Outer frame state.
return SetOutput(node, MachineRepresentation::kTagged);
}
从这个函数中我们可以看出来FrameSTate Node有6个期望的输入:
- paramters:UseInfo is Anytagged
- registers:UseInfo is Anytagged
- accumulator:UseInfo is Any
- context:UseInfo is AnyTagged
- closure:UseInfo is AnyTagged
- other FrameState:UseInfo is AnyTagged
每个UseInfo都包括两个部分:Truncation和Representation。
Truncation:意味着这个Node所产生的值的哪一部分将被使用,如果Turncation是kWord32那么就意味着,这个Node所产生的值的低32位的部分将被使用,也就是被截断为32位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
enum class TruncationKind : uint8_t { kNone, kBool, kWord32, kWord64, kOddballAndBigIntToNumber, kAny };
Representation:代表了将以什么样的格式使用这个值,如果是kWord64那么就意味着需要将这个值转换为64位使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
enum class MachineRepresentation : uint8_t { kNone, kBit, kWord8, kWord16, kWord32, kWord64, kTaggedSigned, // (uncompressed) Smi kTaggedPointer, // (uncompressed) HeapObject kTagged, // (uncompressed) Object (Smi or HeapObject) kCompressedPointer, // (compressed) HeapObject kCompressed, // (compressed) Object (Smi or HeapObject) // FP representations must be last, and in order of increasing size. kFloat32, kFloat64, kSimd128, kFirstFPRepresentation = kFloat32, kLastRepresentation = kSimd128 };
如果Truncation是kWord32然后Representation是kWord64那么就意味着这个Node产生的值的低32位将被截断之后转为64位给user使用,顺嘴提一下Node的output representation代表的是这个Node所产生的值的格式。
以AnyTagged举例,它的Truncation是Any也就是没有Truncation,而Tagged代表的是将以Tagged的形式(smi或者heapobject)使用这个值。而值为Any的UesInfo就意味着没有Truncation也没有Representation。到这里我们已经知道了在SL阶段,对于FrameState Node的处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// The {UseInfo} class is used to describe a use of an input of a node.
static UseInfo AnyTagged() {
return UseInfo(MachineRepresentation::kTagged, Truncation::Any());
}
// Undetermined representation.
static UseInfo Any() {
return UseInfo(MachineRepresentation::kNone, Truncation::Any());
}
// Value not used.
static UseInfo None() {
return UseInfo(MachineRepresentation::kNone, Truncation::None());
}
在上面的Poc所生成的SoN中一共有两个FrameState Node,我们所关注的是第二个Framstate,与x + y产生的CheckPoint(在EffectLinearization阶段被简化成DeoptimizeIf)绑定的FrameState Node。

其中问题出在第三个Input的处理上,第三个Input的UseInfo是Any,且从SoN中可以看出来第三个Input是BigIntAsUintN[64] Node,现在知道的是:
- FrameState的3rd Input的期望Representation是MachineRepresentation::kNone(从Any的UseInfo可知)。
- FrameState的3rd Input的Truncation是Any。
- 而3rd Input的Out_rep是kWord64(在Retype阶段获得)。
1 2 3 4 5
case IrOpcode::kBigIntAsUintN: { ProcessInput(node, 0, UseInfo::TruncatingWord64()); SetOutput(node, MachineRepresentation::kWord64, Type::BigInt()); return; }
在Truncation Propagation进行截断的传播之后,继续向前走看一下Lowering阶段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
ZoneVector<MachineType>* types =
new (zone->New(sizeof(ZoneVector<MachineType>)))
ZoneVector<MachineType>(1, zone);
(*types)[0] = DeoptMachineTypeOf(GetInfo(accumulator)->representation(),
TypeOf(accumulator));
node->ReplaceInput(
2, jsgraph_->graph()->NewNode(jsgraph_->common()->TypedStateValues(
types, SparseInputMask::Dense()),
accumulator));
在这个阶段并没有像处理其他Node一样使用convertInput()为accumulator转换格式(这里实际上漏洞问题所在),而是为FrameState的accumulator这个Input计算MachineType。
MachineType的作用是什么呢?因为FrameState是为了重建Interpreted Frame而存在的每个Input都代表了Input Frame的一个值,所以MachineType是为了在转换Frame时搞清楚每个值的格式(kWord64)和语义(kInt64)。在计算完成后在3rd Input和FrameState Node之间插入一个TypedStateValues Node,代表这个值已经是拥有类型的了。在SL完成之后SoN变成下面的样子:
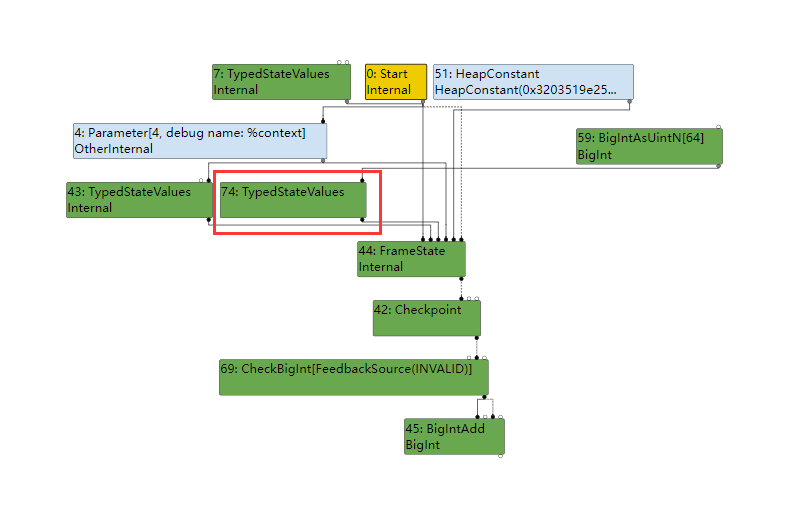
而生成的MachineType是AnyTagged,代表accmulator的值在Input Frame中是以tagged形式存在:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
static MachineType DeoptMachineTypeOf(MachineRepresentation rep, Type type) {
// ..
if (rep == MachineRepresentation::kWord64) {
if (type.Is(Type::BigInt())) {
return MachineType::AnyTagged();
}
// ...
}
问题出现了,accumulator的Input是BigIntAsUint这个node,这意味着实际上输入是BigInt代表的真实数值,如果是BigInt(15)那么实际上Input就是15,这个值就是raw number不是Tagged形式,为它打上Tagged这样的MachineType,导致在Deoptimization直接将这个值当成Tagged smi或者Tagged heapobject使用!所以修补方法也可以想象到,就是Input和FrameState这两个node之间插入一个转换的node将它重新转回BigInt,这样Input就是一个Tagged值了。
在SL阶段之后进入将会进入EffectLinearization阶段,BigIntAsUintN[64]将被简化成Int64Constant[15]:

然后略过剩余的部分,直到code generation阶段为Deoptimization生成Translation,为这一次的Deoptimize生成Translation,下面是处理accumulator部分的代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
void CodeGenerator::AddTranslationForOperand(Translation* translation,
Instruction* instr,
InstructionOperand* op,
MachineType type) {
case Constant::kInt64:
DCHECK_EQ(8, kSystemPointerSize);
if (type.representation() == MachineRepresentation::kWord64) {
literal =
DeoptimizationLiteral(static_cast<double>(constant.ToInt64()));
} else {
// When pointers are 8 bytes, we can use int64 constants to represent
// Smis.
DCHECK_EQ(MachineRepresentation::kTagged, type.representation());
Smi smi(static_cast<Address>(constant.ToInt64()));
DCHECK(smi.IsSmi());
literal = DeoptimizationLiteral(smi.value());
}
break;
解释一下上面的这段代码:
首先accumulator的Node在EffectLinearization阶段由BigIntAsUintN[64]简化成Int64Constant[15],而在code generation之前的instruction slelction阶段这个Node会被转化为立即数imm保存在一个imm表中。
![image-20220719144915501]()
因为是Int64Constant Node所以operand的类型也是Int64,之前已经为accumulator的TypedStateValue计算出MachineType,根据MachineType可能有两种情况:
- 如果MachineType是kWord64,那么这个Int64整个就作为一个64位的有符号值使用。
- 而如果MachineType是其他的表示,尤其是Tagged,那么这个Int64可能是一个Tagged smi。
在这个例子中前面已经说过这个TypedStateValue已经被打上Tagged的类型,这样就会去第二个分支执行:15将被当作一个tagged smi使用,并从中取出smi具体的值,15右移32位结果将会变成0。这个值将被放入到Translation中在Deoptimization中使用。
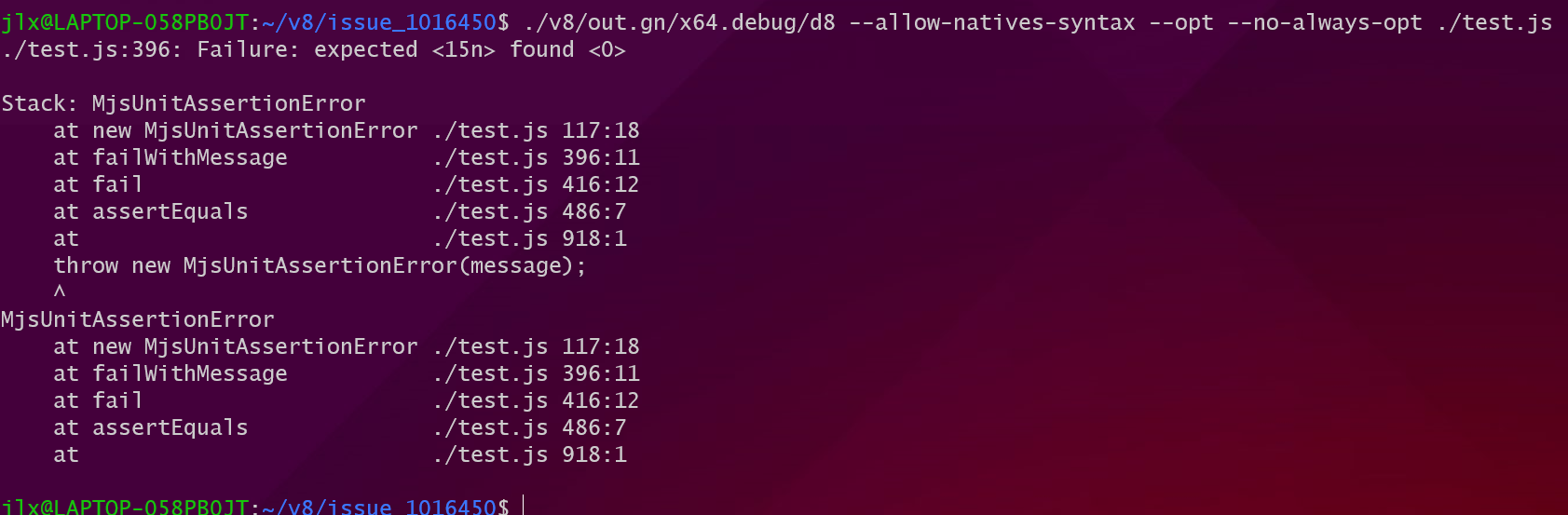
结果就是当触发Deoptimization时,根据Translation,这个0将被当作accumulator的值放入到accumulator中进行后续计算(这里本来应该使用15的BigInt进行计算)。在Poc中导致的结果就是x + y,y最终变成0。
从运行的结果中也可以看出来本来应该是15n,但是最后计算结果是0:
patch分析
所以这个漏洞应该如何修补呢?导致这个漏洞的原因是:BigIntAsUintN这个Node所计算得到的kWord64的值应该被转换为BigInt而不应该以kWord64继续存在。如果kWord64的值被转换为BigInt,就不会出现在Deoptimization时把15当成Taged Value,并把从15这个”Tagged Value”中提取出的0直接作为accumulator的值的情况,而应该是拿着15转换得到的BigInt的地址当作accumulator的值。
具体到代码层面有两个问题:
在Lowering阶段没有对accmulator的格式进行转换,缺少一个
convertInput()。在Propagate阶段,accumulator的UseInfo是Any,这样导致ConvertInput不会对accumulator进行格式转换:
1 2 3 4 5 6
void ConvertInput(Node* node, int index, UseInfo use, Type input_type = Type::Invalid()) { Node* input = node->InputAt(index); // In the change phase, insert a change before the use if necessary. if (use.representation() == MachineRepresentation::kNone) return; // No input requirement on the use.
最终v8官方的patch如下:
修改了FrameState的accumulator这个Input的UseInfo为AnyTagged,还在Lowering阶段添加了convertInput(),这样在convertInput()中就会为accumulator插入一个转换Node将Uint转换为BigInt。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
diff --git a/src/compiler/simplified-lowering.cc b/src/compiler/simplified-lowering.cc
index 2e8f40f..abbdae3 100644
--- a/src/compiler/simplified-lowering.cc
+++ b/src/compiler/simplified-lowering.cc
@@ -1197,7 +1197,7 @@
// TODO(nicohartmann): Remove, once the deoptimizer can rematerialize
// truncated BigInts.
if (TypeOf(input).Is(Type::BigInt())) {
- ProcessInput(node, i, UseInfo::AnyTagged());
+ ConvertInput(node, i, UseInfo::AnyTagged());
}
(*types)[i] =
@@ -1220,11 +1220,22 @@
// Accumulator is a special flower - we need to remember its type in
// a singleton typed-state-values node (as if it was a singleton
// state-values node).
+ Node* accumulator = node->InputAt(2);
if (propagate()) {
- EnqueueInput(node, 2, UseInfo::Any());
+ // TODO(nicohartmann): Remove, once the deoptimizer can rematerialize
+ // truncated BigInts.
+ if (TypeOf(accumulator).Is(Type::BigInt())) {
+ EnqueueInput(node, 2, UseInfo::AnyTagged());
+ } else {
+ EnqueueInput(node, 2, UseInfo::Any());
+ }
} else if (lower()) {
+ // TODO(nicohartmann): Remove, once the deoptimizer can rematerialize
+ // truncated BigInts.
+ if (TypeOf(accumulator).Is(Type::BigInt())) {
+ ConvertInput(node, 2, UseInfo::AnyTagged());
+ }
Zone* zone = jsgraph_->zone();
- Node* accumulator = node->InputAt(2);
if (accumulator == jsgraph_->OptimizedOutConstant()) {
node->ReplaceInput(2, jsgraph_->SingleDeadTypedStateValues());
} else {
@@ -1237,7 +1248,7 @@
node->ReplaceInput(
2, jsgraph_->graph()->NewNode(jsgraph_->common()->TypedStateValues(
types, SparseInputMask::Dense()),
- accumulator));
+ node->InputAt(2)));
}
}
patch之后再运行Poc,可以发现在SL结束后BigIntAsUintN后面都会被插入一个ChangeUint64ToBigInt Node:

这样BigInt的值就会被包装起来,然后在构建Translation的时候执行的是下面这一部分的代码,在Deoptimization结束后传入的是BigInt的地址:
1
2
3
4
case Constant::kHeapObject:
DCHECK_EQ(MachineRepresentation::kTagged, type.representation());
literal = DeoptimizationLiteral(constant.ToHeapObject());//finally get this place
break;
利用分析
除了像上面的Poc一样使用Constant 15n 可以导致错误的计算结果(计算结果更小了,没有办法构造溢出)之外,如果将asUintN()的第一个参数改的更小,那么在EffectLinearization阶段BigIntAsUintN将会被简化成下面的样子:
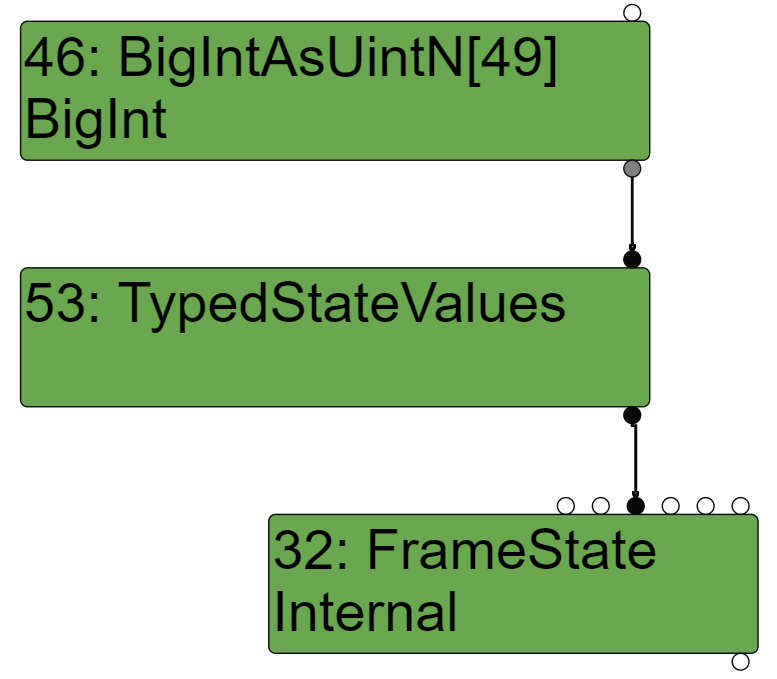
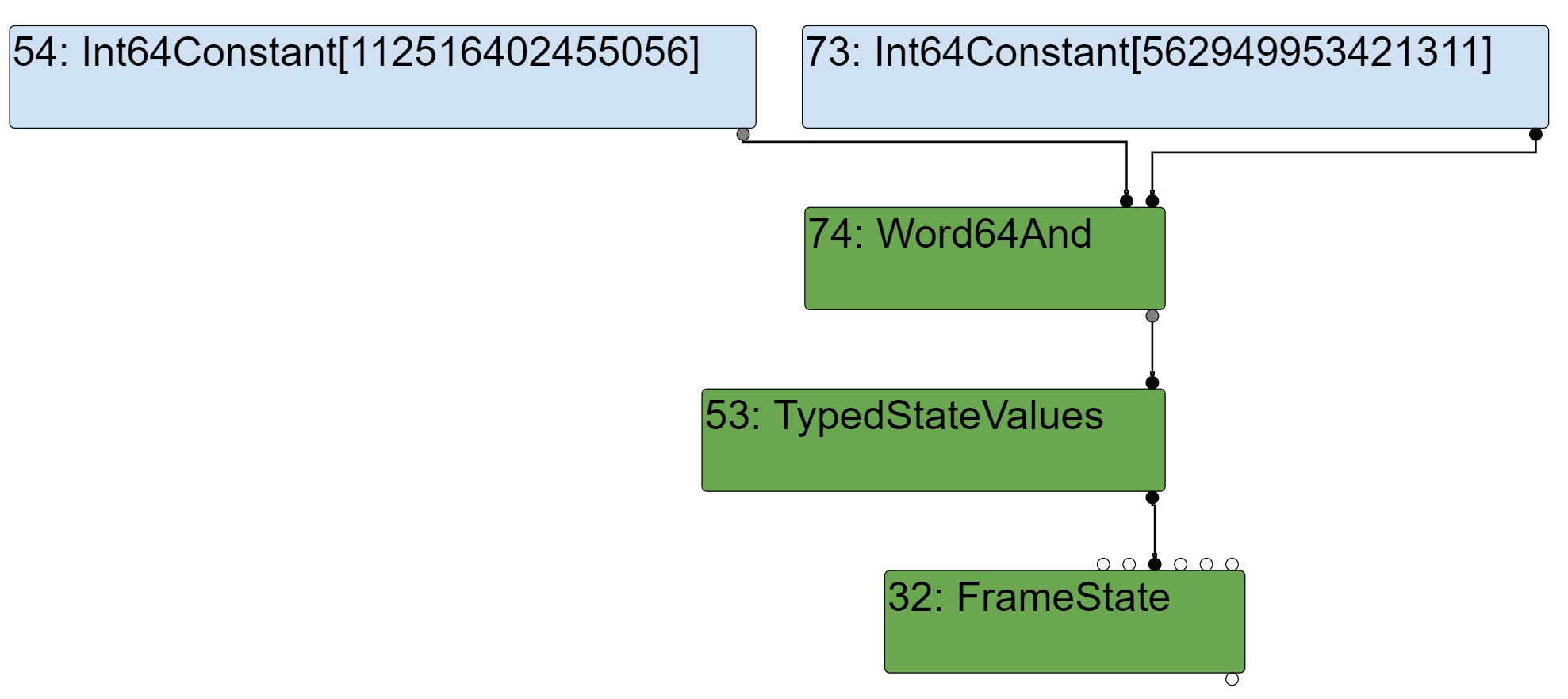
这样accumulator就不在是一个imm,不是一个Constant,在Input Frame中它可能被保存在栈中或者寄存器中,那么在构建Translation的时候,会将这个值标记为STACK_SLOT或者REGESITER:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
void CodeGenerator::AddTranslationForOperand(Translation* translation,
Instruction* instr,
InstructionOperand* op,
MachineType type) {
//[...]
else if (op->IsRegister()) {
InstructionOperandConverter converter(this, instr);
if (type.representation() == MachineRepresentation::kBit) {
translation->StoreBoolRegister(converter.ToRegister(op));
} else if (type == MachineType::Int8() || type == MachineType::Int16() ||
type == MachineType::Int32()) {
translation->StoreInt32Register(converter.ToRegister(op));
} else if (type == MachineType::Uint8() || type == MachineType::Uint16() ||
type == MachineType::Uint32()) {
translation->StoreUint32Register(converter.ToRegister(op));
} else if (type == MachineType::Int64()) {
translation->StoreInt64Register(converter.ToRegister(op));
} else {translation->StoreRegister(converter.ToRegister(op));
}
}
//[...]
}
这样我们传入的第二个参数不用再转换成smi然后再提取其中的值再被传入accumulator中,而是直接从寄存器或者栈中读入到accumulator。比如向accumulator中传入了0x111111111,那么这个值将会被当成一个obejct的地址使用,这意味这我们获得了fakeobj这样的原语。但是可惜的是不存在信息泄露,否则这个漏洞就可以通过泄露 + fakeobj任意伪造object。